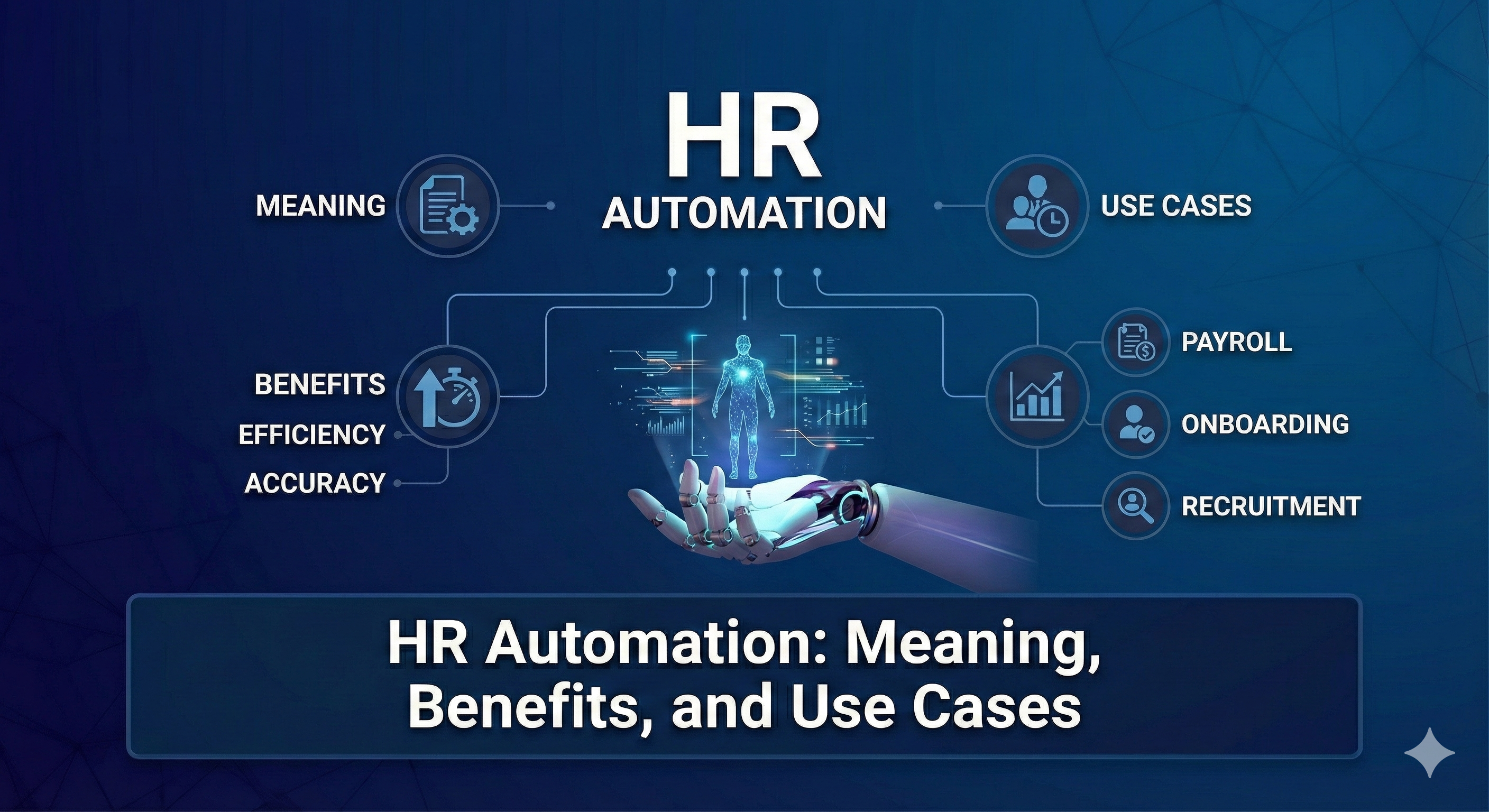
What Is an HRMS? Meaning, Features, Benefits & Examples

Why HRMS Has Become a Strategic Imperative for Leadership
In today’s competitive and compliance-driven business environment, people management is no longer an operational concern is a board-level priority. As organizations scale, expand geographically, and adopt hybrid work models, traditional HR practices struggle to keep up with complexity, compliance, and speed.
This is where an HRMS becomes critical.
A modern HRMS (Human Resource Management System) enables leadership teams to move beyond fragmented HR processes and build a centralized, intelligent, and data-driven people ecosystem. For CXOs, founders, and HR leaders, understanding what an HRMS is, how it works, and why it matters is essential for sustainable growth.
This guide offers a complete executive-level understanding of HRMS meaning, features, benefits, and examples, helping decision-makers evaluate HRMS software not just as a tool—but as a strategic investment.
What Is an HRMS? Meaning Explained for Business Leaders
An HRMS, or Human Resource Management System, is an integrated software platform designed to manage every aspect of an organization’s workforce through a single, unified system. It brings together employee data, payroll, attendance, compliance, performance, and analytics under one digital roof.
From a leadership standpoint, the meaning of HRMS goes far beyond HR administration. It represents a shift from reactive people management to proactive workforce governance. An HRMS allows organizations to standardize policies, automate repetitive tasks, reduce compliance risks, and generate insights that directly influence business strategy.
In essence, an HRMS system transforms HR from a support function into a strategic enabler of growth, efficiency, and accountability.
Understanding HRMS vs HRIS vs HCM
Many executives encounter confusion around HR technology terminology. While HRIS, HRMS, and HCM are often used interchangeably, their scope differs.
An HRIS primarily focuses on storing employee information and managing administrative records. An HRMS expands this capability by incorporating payroll, compliance, attendance, and workflow automation. HCM platforms go a step further by emphasizing long-term talent strategy, workforce planning, and advanced analytics.
For most growing organizations, an HRMS software solution offers the optimal balance—delivering operational efficiency while still supporting strategic decision-making without unnecessary complexity.
Why HRMS Matters at the C-Suite Level
For leadership teams, implementing an HRMS system is not about digitization alone is about control, visibility, and risk management.
A centralized HRMS provides executives with real-time access to workforce data, allowing them to monitor payroll costs, attrition trends, compliance status, and productivity metrics across departments or locations. This visibility enables faster, more confident decision-making.
Moreover, HRMS platforms reduce dependency on manual processes, which are often prone to errors, delays, and compliance gaps. By automating core HR functions, organizations significantly lower operational risk while improving internal governance.
Core HRMS Features Explained in Depth
Employee Information Management: The Foundation of HRMS
At the heart of every HRMS software lies a centralized employee database. This module consolidates all employee information—personal details, employment history, documents, and role assignments into a single system of record.
For leadership, this eliminates data silos and ensures consistency across HR, finance, and compliance teams. Accurate data also becomes the backbone for analytics, audits, and workforce planning.
Payroll & Compliance Management: Accuracy Meets Accountability
Payroll is one of the most sensitive HR functions, directly impacting employee trust and legal compliance. A robust HRMS system automates payroll calculations, tax deductions, statutory filings, and payslip generation.
In regions like India, where compliance requirements frequently change, HRMS platforms such as JioHRMS are designed to align payroll processes with current statutory regulations. This ensures timely compliance while reducing manual intervention and dependency on external consultants.
Attendance, Leave & Workforce Scheduling
Attendance and leave management are no longer limited to punch-in and punch-out systems. Modern HRMS features include biometric integration, remote attendance tracking, automated leave accruals, and shift scheduling.
From a leadership perspective, this provides transparency into workforce availability, overtime costs, and productivity patterns—particularly critical for distributed or shift-based teams.
Recruitment & Onboarding: Speed with Structure
An HRMS streamlines recruitment by integrating applicant tracking, interview workflows, offer management, and onboarding into a single process. This reduces hiring timelines while ensuring consistency in candidate experience.
For fast-growing organizations, this structured approach to hiring ensures scalability without compromising quality or compliance.
Performance Management & Goal Alignment
Performance management within an HRMS moves beyond annual appraisals. Continuous feedback, goal tracking, and performance analytics allow leaders to align individual objectives with organizational priorities.
This visibility supports merit-based decisions, leadership development, and succession planning.
Analytics & Dashboards: Turning HR Data into Business Intelligence
One of the most valuable HRMS benefits for executives is access to actionable insights. HR dashboards translate workforce data into visual metrics—attrition rates, payroll trends, headcount growth, and compliance status.
These insights empower CXOs to anticipate challenges rather than react to them.
Strategic Benefits of HRMS for Organizations
The implementation of an HRMS system delivers both immediate operational benefits and long-term strategic value.
Operationally, automation reduces HR workload, improves accuracy, and shortens processing cycles. Strategically, HRMS platforms enable leadership teams to make data-driven decisions about hiring, retention, cost optimization, and workforce planning.
Additionally, a well-implemented HRMS enhances employee experience by providing transparency, self-service access, and timely communication—factors that directly influence retention and employer brand perception.
HRMS Examples Across Business Stages
In startups, HRMS software helps founders manage payroll, compliance, and hiring without building large HR teams.
For SMEs, HRMS platforms support structured growth, performance management, and multi-location operations.
At the enterprise level, HRMS systems enable governance, analytics, and workforce optimization at scale.
Solutions like JioHRMS demonstrate how a single platform can adapt across these stages while maintaining simplicity and control.
How to Choose the Right HRMS Software
Selecting the right HRMS software requires evaluating more than just features. Leadership teams should assess scalability, compliance readiness, data security, analytics capability, and vendor reliability.
An effective HRMS should grow with the organization while minimizing disruption during expansion or regulatory changes.
The Future of HRMS: What Leaders Should Prepare For
The future of HRMS platforms lies in intelligent automation, predictive analytics, and deeper integration with finance and business systems. AI-driven insights will further enhance workforce planning, attrition prediction, and skill development.
Organizations that invest early in modern HRMS systems will be better positioned to manage talent complexity and remain competitive.
Make your HR Software fun and easy!
Learn how Jio HR Software can help you automate HR processes and stay 100% compliant.
Final Call to Action
As organizations grow, people operations become more complex—and more critical. Relying on disconnected systems or manual processes increases risk and limits visibility.
A modern HRMS system helps leadership teams build resilient, compliant, and insight-driven organizations.
If your business is preparing for its next stage of growth, now is the time to evaluate how an HRMS can support that journey—strategically, not just operationally.
 What Is an HRMS? Meaning Explained for Business Leaders
What Is an HRMS? Meaning Explained for Business Leaders