Human Resource Management System: Functions & Objectives

In today’s enterprise landscape, organizations are not defined solely by their products, capital, or technology. They are defined by how effectively they manage their people. As businesses scale, diversify, and operate across regulatory and geographical boundaries, managing human capital through manual or fragmented systems becomes unsustainable.
This is where a Human Resource Management System plays a critical role.
A modern human resource management system is no longer an operational convenience. It is a strategic enterprise platform that enables leadership teams to govern workforce operations, control risk, drive productivity, and align people strategy with long-term business objectives.
This guide is written for CXOs, founders, and senior leadership teams who want a comprehensive understanding of the functions and objectives of a human resource management system, and how it supports sustainable, compliant, and scalable growth.
What Is a Human Resource Management System?
A human resource management system (HRMS) is an integrated digital platform that manages the complete employee lifecyclefrom hiring to exitwithin a single, centralized system.
Unlike standalone HR tools, a human resource management system brings together:
Employee records
Payroll and compensation data
Attendance and leave information
Performance evaluations
Compliance documentation
By acting as a single source of truth, HRMS ensures accuracy, consistency, and transparency across the organization. For leadership teams, this centralized control is essential for governance, audit readiness, and strategic planning.
Why Human Resource Management Systems Matter to the C-Suite
From a leadership perspective, HR is one of the largest operational and financial levers in the organization. Workforce costs, compliance obligations, and talent retention directly affect margins, reputation, and growth.
A strategically implemented human resource management system enables CXOs to:
Gain real-time visibility into workforce metrics
Reduce payroll, compliance, and attrition risks
Improve organizational productivity and accountability
Align talent initiatives with business goals
Make data-backed decisions instead of intuition-driven ones
In this context, HRMS becomes a decision-support system, not just an HR tool.
Evolution of HR System Software
Understanding the evolution of HR system software helps leadership appreciate the value of modern HRMS platforms.
Early Stage: Manual HR Operations
HR processes were paper-based or spreadsheet-driven, resulting in inefficiencies, errors, and compliance exposure.
Intermediate Stage: Disconnected HR Tools
Organizations adopted digital payroll or attendance systems, but these operated in silos, limiting insight and control.
Integrated Stage: Human Resource Management Systems
HRMS unified data and workflows, bringing standardization and automation.
Advanced Stage: Intelligent HRMS
Today’s HRMS platforms incorporate analytics, automation, and AI to provide predictive workforce intelligence.
Most high-growth organizations now operate in this advanced stage.
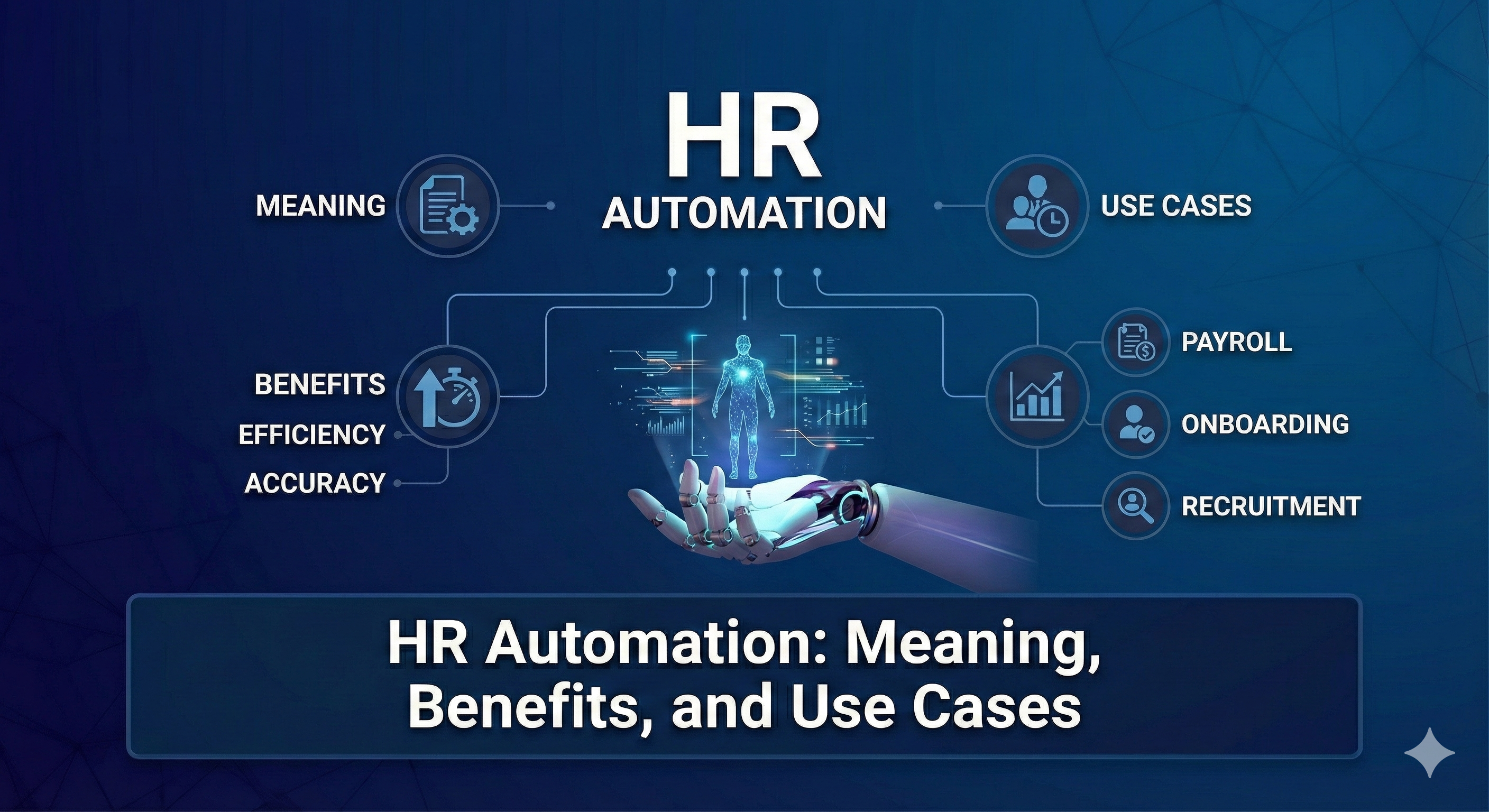
Core Functions of a Human Resource Management System
Understanding HR management system functions clarifies how HRMS delivers value across the organization.
Talent Acquisition and Recruitment
A human resource management system streamlines recruitment by managing job postings, applicant tracking, interview workflows, and offer management within a single system.
This structured approach reduces hiring timelines, improves candidate experience, and ensures consistency in talent selection.
Employee Onboarding and Lifecycle Management
Effective onboarding directly impacts retention and productivity. HRMS digitizes onboarding processes, documentation, and role-based task assignments.
Beyond onboarding, lifecycle management ensures smooth handling of promotions, transfers, role changes, and exits without data loss or compliance gaps.
Payroll and Compensation Management
Payroll accuracy is both a financial and trust issue. Modern HR system software automates payroll calculations, tax deductions, and statutory compliance.
Compensation management tools help leadership design fair, transparent, and performance-aligned pay structures.
Time, Attendance, and Leave Management
Accurate attendance tracking is critical for payroll accuracy and workforce planning. HRMS supports automated attendance, shift management, and leave approvals based on predefined policies.
This reduces disputes, improves transparency, and strengthens internal trust.
Performance Management
Performance management has evolved from annual appraisals to continuous development. HRMS enables goal tracking, ongoing feedback, and structured performance reviews.
Leadership gains visibility into productivity trends, high performers, and skill gaps across teams.
Learning and Development
A future-ready workforce requires continuous upskilling. HRMS supports training programs, skill tracking, and certification management, ensuring talent development aligns with organizational goals.
Compliance and Risk Management
One of the most critical HRMS objectives is compliance assurance. HRMS automates statutory reporting, policy enforcement, and audit readiness, reducing legal and financial risk.
HR Analytics and Workforce Intelligence
Advanced HRMS platforms convert workforce data into actionable insights. Leadership can analyze attrition patterns, engagement levels, productivity metrics, and future workforce needs.
This transforms HR into a strategic intelligence function.
Primary Objectives of a Human Resource Management System
The HRMS objectives define why organizations invest in these platforms.
Operational Efficiency
Automation reduces manual effort, errors, and delays, freeing HR teams to focus on strategic initiatives.
Governance and Compliance
Built-in controls ensure consistent policy enforcement and regulatory adherence.
Improved Employee Experience
Employee self-service portals improve transparency, autonomy, and engagement.
Strategic Decision Support
HR analytics enables informed leadership decisions related to workforce planning and cost optimization.
Scalable Growth Enablement
A modern human resource management system supports organizational growth without increasing administrative complexity.
Human Resource Management System vs Traditional HR Tools
Why Cloud-Based HRMS Is the Preferred Choice
Cloud-based HR system software offers faster deployment, lower infrastructure costs, continuous upgrades, and enterprise-grade security. For growing organizations, it ensures flexibility without sacrificing control.
How JioHRMS Aligns with Modern HRMS Objectives
JioHRMS is designed to address the real-world challenges faced by growing and enterprise organizations:
Centralized employee data management
Integrated payroll and compliance workflows
Structured attendance and performance tracking
Real-time HR analytics for leadership visibility
The focus is on enabling structured, compliant HR operations while supporting leadership-level decision-making without unnecessary complexity.
Future Outlook: Where Human Resource Management Systems Are Headed
The next generation of HRMS will emphasize predictive analytics, AI-driven workforce planning, personalized employee experiences, and ESG-focused reporting.
Organizations that invest early in robust HRMS frameworks gain long-term strategic advantage.
Final Thoughts for Business Leaders
A human resource management system is no longer an operational upgradeit is a leadership necessity. When implemented thoughtfully, HRMS strengthens governance, improves workforce outcomes, and supports sustainable growth.
For CXOs, the right HRMS is not about software adoption. It is about building a resilient people infrastructure.
 What Is a Human Resource Management System?
What Is a Human Resource Management System?