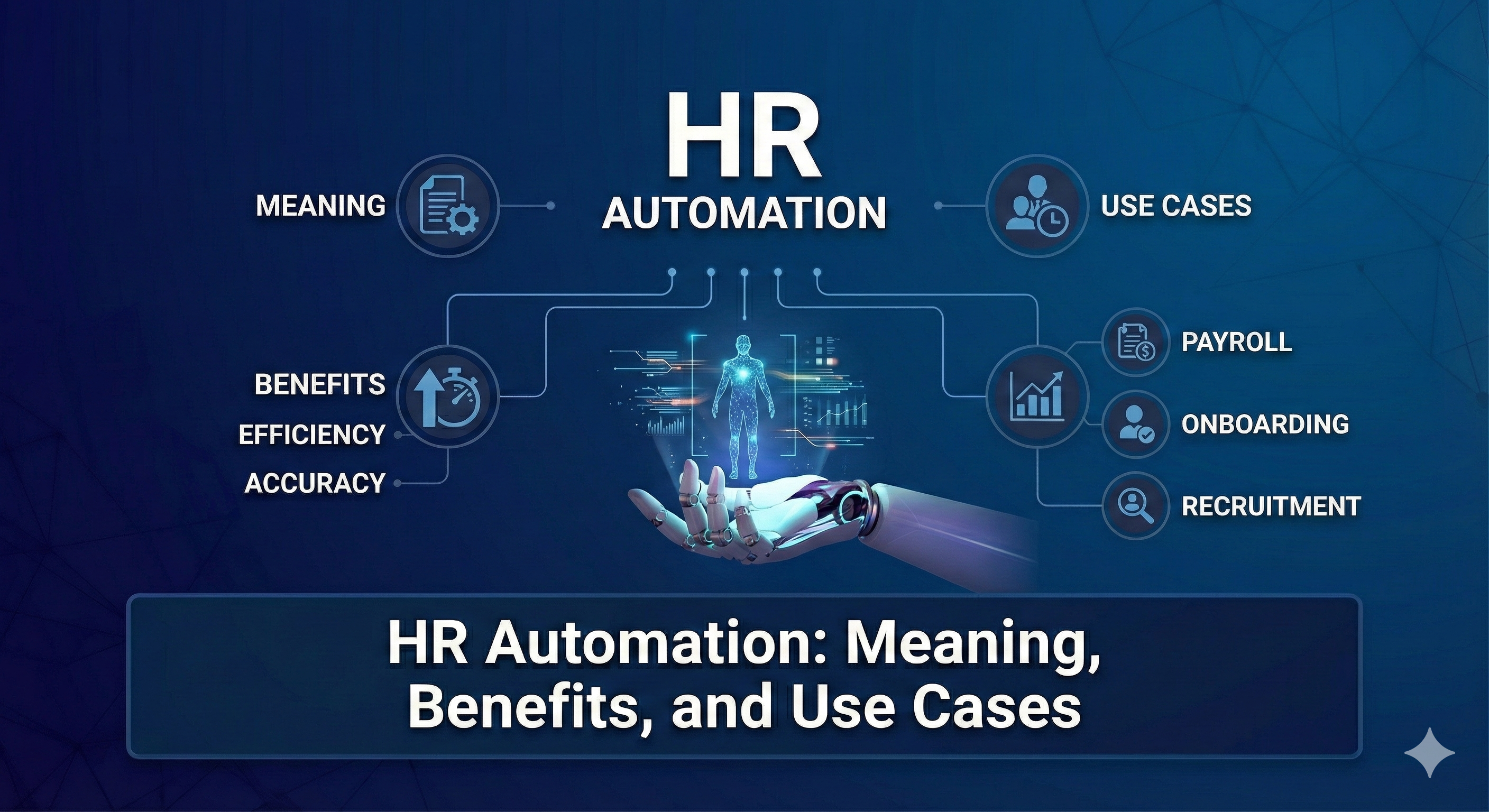
Understanding the Basics: What Are HRMS, HRIS & HCM?

In today’s fast-paced digital economy, organizations rely heavily on robust HR ecosystems to manage people, processes, and performance. But what exactly differentiates HRMS vs HRIS vs HCM? Though these terms are sometimes used interchangeably, they represent distinct scopes of functionality and strategic impact.
Let’s demystify these systems with clarity, depth, and practical insights for C-suite leaders responsible for technology investments and organizational velocity.
What is HRIS (Human Resource Information System)?
HRIS (Human Resource Information System) refers to software that centralizes essential employee data and automates HR administrative processes.
Core Features of HRIS
Employee records and personal data
Job titles, departments, and org structure
Attendance and leave tracking
Reporting and compliance
Policy management and employee self-service
Primary Objective: Maintain accurate employee data and streamline HR operations.
Best Use Cases for HRIS
Small to mid-sized businesses
Companies needing centralized personnel data
Organizations prioritizing core HR reporting
Example Insight: Unlike traditional manual systems, an HRIS reduces administrative burden by offering a single source of truth, increasing accuracy, and minimizing risks associated with outdated data.
Looking for the Best Online HR Software? Check out the Best Online HR Software .
What is HRMS (Human Resource Management System)?
HRMS (Human Resource Management System) extends beyond basic HRIS functionalities to encompass more operational aspects of workforce management.
HRMS Capabilities
All standard HRIS functions
Payroll processing and benefits administration
Time and attendance tracking
Leave & shift management
Expense and reimbursement workflows
Integration with finance & accounting systems
Primary Objective: Streamline HR administration and workforce operations for smoother execution.
Why HRMS Matters
For dynamic organizations juggling large workforces, an HRMS becomes indispensable. With advanced automation, HR teams can reduce errors, increase operational transparency, and cut processing time significantly.
What is HCM (Human Capital Management)?
HCM (Human Capital Management) represents the most comprehensive approach to managing people across the employment lifecycle from recruiting to retirement.
HCM Core Domains
Talent acquisition and onboarding
Performance and competency management
Learning & development
Succession planning
Workforce analytics and strategy
Compensation and rewards optimization
Primary Objective: Align workforce capabilities with business strategy for growth, innovation, and long-term competitiveness.
Why HCM Is Strategic
While HRIS and HRMS handle administrative and operational tasks, HCM is inherently strategic enabling leadership to make data-driven decisions that elevate organizational performance.
HRMS vs HRIS vs HCM: Detailed Comparison
To help you gain a comprehensive grasp, below is a comparison across key dimensions most relevant to senior leadership:
Insight for Leaders
Startups & SMBs: HRIS can be sufficient initially.
Growing Enterprises: HRMS offers scalability and efficiency.
Large Corporations: HCM supports strategic workforce transformation.
HR Software Comparison Framework for Today’s Enterprises
Selecting the right HR software isn’t just about features it’s about strategic fit.
1. Functional Scope
HRIS: Efficient administrative engine
HRMS: Operational powerhouse
HCM: Strategic intelligence system
C-Suite Evaluation Tip: Ensure alignment between organizational strategy and the chosen platform’s capabilities.
2. Integration & Interoperability
Modern enterprises demand seamless data flow across systems including finance, ERP, CRM, and productivity tools.
✨ Best Practice: Choose systems with open APIs and strong integration ecosystems.
3. Analytics, Reporting & Insights
HRIS delivers static dashboards
HRMS offers operational reporting
HCM enables predictive analytics and workforce modeling
C-Level Insight: Workforce analytics drives retention, talent optimization, and future readiness.
4. User Experience & Adoption
The best platforms combine intuitive interfaces with employee self-service, reducing helpdesk tickets and enhancing satisfaction.
5. Mobile & Remote Capabilities
With hybrid and remote work becoming standard, mobile accessibility is essential for employee engagement and operational execution.
Role of AI and Analytics in HRMS, HRIS & HCM
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer optional it’s fundamental.
AI in HR Software
Predictive attrition models
Talent matching and skills forecasting
Natural language processing for candidate evaluation
Intelligent scheduling and workload balancing
Why This Matters for C-Suite: AI amplifies HR productivity and strategic foresight turning data into action.
 What is HRIS (Human Resource Information System)?
What is HRIS (Human Resource Information System)?